 |
 |
 |
|
Home | 500 YouTube Videos, 25 topics in 2 parts | Video page Cancer to last topic science | VIDEOS YouTube on Economic-political Issues | Documentaries, Most view on YouTube, What I've learned | Concise: Diets, health, weight, insulin resistance, and type 2 diabetes | Part 1: Cardiovascular disease causes | Part 2: CVD Myths: Fats, sugars, cholesterol, and Statins id2.html | Part 3:: Carbohydrates: types, tables, role in NAFLD & MeS | Part 4 Fats role in CVD | Rancid Polyunsaturated and Trans-fats are Bad | Part 5: Healthful Lifestyle, Diet, Supplements, & Drugs | Part 6: Ill-health pandemic: conditons, causes, and dietary fixes | Atkins Low Carb Diet with modifications | Diabetes meds, bad medicines | Evidence for Alternate Day Fasting--Cures diabetes | Terms used in dietary articles | Pharma's tobacco science, diet, Inuslin Resistance, diabetes | Best Healthful Supplement for seniors | Fasting cures type 2 diabetes
|
|
 |
|
Recommended Healthful
|
|
Part 4 Fats role in CVD
|
 |
 |
|
| transports fats and cholesterol from intestines |
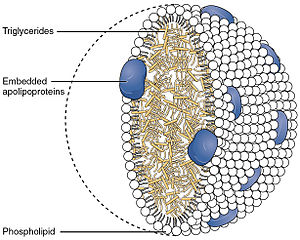
|
| Low Density Lipoprotein; transport from liver |
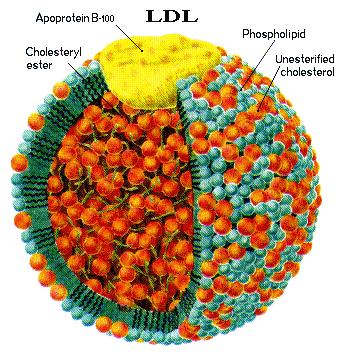
|
The page and the subsequent 8 parts are being
updated so as to better account for the evidence of infective agents in the
cardiovascular disease process. It will be completed
by October of 2015. For the evidence in support of
infection in the artery walls, for an evaluation of the cholesterol myth
Part 4 Fats
role in CVD http://healthfully.org/rh/id4.html
(8/23 /15)
|
AS Atherosclerosis
|
|
N3
Omega 3 fatty acids
|
|
CVD Cardiovascular
disease
|
|
N6
Omega 6 fatty acids
|
|
HT
Hypertension
|
|
MeS Metabolic
syndrome[1][1]
|
|
IR
Insulin resistance
|
|
NALFD Non-alcoholic fatty
liver disease
|
|
KOL Key
opinion leader
|
|
T2D
Type 2 Diabetes
|
|
MI
Myocardial infarction
|
|
TC
Total Cholesterol
|
Background: Building on Part 1
the cause of
cardiovascular disease (CVD) was not dyslipidemia, but rather
reactive chemicals damaging LDL within the muscular part of the artery wall and
the subsequent immune response which resulted in atherosclerosis (AS).
Part
1
went to list the vital roles
of cholesterol and that lowering
cholesterol levels does not prevent CVD
since it doesn’t prevent atherosclerosis (AS).
Part
2
follows from part 1; it sets out the cholesterol myth (that cholesterol does
not cause CVD) and thus using
statins to lower cholesterol not only doesn’t prevent CVD or AS, but given the
importance of cholesterol and other products of the mevalonate pathway, that disruption by statins of the
synthesis of these essential bioactive chemicals is a very bad idea, especially
for the elderly. Part 3 is on the role of carbohydrates through glycation
and oxidative
products of metabolism that is the leading causal factor for AS
and CVD, and an assortment of chronic
age-related conditions. First among
the carbohydrates is fructose,
which is one half of the disaccharide sucrose.
Fructose in high amounts damages the liver which leads to the
development of insulin resistance (IR)
and metabolic syndrome (MeS)--how. We will be exploring the fat myths.
Saturated Fats are safer than carbohydrates: in 11 out of 12 studies reviewed in Wikipedia, results did not show
a benefit from low fat, or increased ratio of polyunsaturated fats
“A meta-analysis of 21
studies considered the effects of
saturated fat intake and found that Intake of saturated fat was not associated
with an increased risk of CHD (coronary heart disease), stroke, or CVD (cardiovascular
disease)" Wiki.
Low fat entails more carbs for energy with
their negative consequences. “Indeed, recent prospective cohort studies have not supported any significant
association between saturated fat intake and cardiovascular risk. Instead, saturated fat has been found
to be protective. The source of the saturated fat may
be important. Dairy foods are exemplary providers of vitamins A and D. As well
as a link between vitamin D deficiency and
a significantly increased risk of cardiovascular mortality, calcium and
phosphorus found commonly in dairy foods may have antihypertensive effects that
may contribute to inverse associations with cardiovascular risk. Meat is another major source of saturated fat. Consumption of processed [luncheon] meats has
been associated with coronary heart disease and diabetes mellitus, which
may be explained by nitrates and sodium
as preservatives “ BMJ
10/22/13. And it gets worse: instead
endpoint deaths and ischemic events,
pharma uses the surrogate endpoint increased serum levels of LDL, Cholesterol,
and triglycerides. However in quality
studies the associate is non-existent or nearly so. “There are no clear
health benefits of replacing
saturated fats with starchy foods (reducing the total amount of fat we eat).
Heart and vascular disease includes heart attacks, angina, strokes, sudden
cardiovascular death and the need for heart surgery” the prestigious Cochrane Review. It get worse, for saturated fats have
been replaced by the unhealthy
polyunsaturated fats, and the recommended low-fat diet entails entails more from
carbohydrates and thus an increase in sugars, which has produced the health
disaster of the Western diet that has cause the obesity, diabetes, and MeS epidemic. Having said all this, there are important
details. For one, that a high carb diet
low on sugar (the traditional diet of Orientals with the high glycemic index
white rice and but 14 grams of sugar does not result in an association with
CVD; and also for tribes on a high carb paleo-diet. As pointed out at http://healthfully.org/rc/id23.html the combination of
high fructose with glucose (mainly from starches) as a steady diet causes a
fatty liver which results in mucking up the metabolic regulatory system. This
and other factors determine risk (see http://healthfully.org/rh/id12.html). Thus like fats, all carbs are not equal, and
lifestyle difference influence risk—click on link.
.   cis-2-butene cis-2-butene
Saturated
fats are best, polyunsaturated fats worse: The truth lies
in the details: one, health science
has
been kicked under the bus by corporate influence which produces tobacco science
and uses its influence in the process and among politicians to promote
financial gains. In particular the
agriculture and manufactured food lobbies have shaped government regulations around
the world, starting with the US in 1977 and UK in 1983 to recommend cutting the
intake of fats by 25% and reducing saturated fats as much as possible on the
bogus claim that they cause dyslipidemia (high serum fatty acids and
triglycerides) and coronary heart disease (CHD). For an excellent historical
thorough recount
of how this happened plus a summation of the benefits of saturated fats, click
on the link to Prof. Miller’s lecture (notes are in supplement
below). However saturated fats don’t go
rancid: they are not subject to
oxidation on the shelf or in your body.
All the carbon bonds are taken—unlike monounsaturated fats such as the
cis and trans-oleic acid shown above and polyunsaturated fats are subject to a
much higher rate of oxidation and glycation[2]. This oxidation
and glycation is called rancidification. Rancid fats cannot be
safely disposed of because
of lack of enzyme for that purpose. They
accumulate in your body and mess up various systems. Moreover they also in the process of their
product give rise to reactive oxygen species (ROS), which cause more
damage. It is to prevent ROS and
rancidification that milk fat is very low in polyunsaturated fats (under 5%)
and so too for beef fat (<10%).
Evolution has set it up so that milk is low in the unhealthful
polyunsaturated fats. And it gets
worse. Polyunsaturated fats are
high in
omega-6 fatty acids and they block the healthful omega-3.
Omega-3 fats (EPA and DHA—not plant ALA)[3]
have important immune system functions.
This unhealthful low omega-3 has many chronic conditions relating to the
immune system. Vegetable oils are
high
in omega-6 and high in polyunsaturated fats.
Nut oils are low in polyunsaturated fats as too are animal sources of
fats. The highly processed vegetable
oils are high in polyunsaturated fats.
Moreover to improve their flavor when used with starches, food
manufactures buy the partially hydrogenated plant fats. Like with rancid fats, they too lack enzymes
for their disposal, and thus contribute to cardiovascular disease.
These are the best kind. Eat more of them and
less carbs. At the end of this paper
this topic is further developed as to diet.
Basics on fatty
acids (fats)
and triglycerides: the dietary significant fats consist
of a chain of 4 to 28 carbon molecules with an organic carboxylic acid group on
the last carbon. Fatty acids are derived
from triglycerides or phospholipids. Each carbon can have 4 single bonds
because
there are just 4 valance electrons. If
the carbon has a double bond with another carbon it is ”unsaturated”, and
“polyunsaturated” with 2 or more double bonds. Having a double bond
entails that there is
only a single hydrogen (see stick drawing above) on each of the carbons in the
double bond; and if they are on the same side it is called “cis” and if on opposite
sides “trans”. Natural trans-fats
occur only in trace amounts. A few polyunsaturated fatty acids are termed
“essential” because they are used to
synthesize a number of important bioactive compounds and they come only from
food sources. They are grouped into
omega-3 (N-3) and omega-6 (N-6)
fatty acids.[4] Compared to carbohydrates
and protein, fatty acids yield the most ATP on an energy per gram basis—9
calories of energy per gram, digestible sugars and starches 4. Free fatty acids
can be converted to
triglycerides and stored in adipose tissue.
“They are consumed in the mitochondria to produce ATP through beta oxidation, whereby they generate acetyl-coA, which enters the citric acid cycle, and NADH andFADH2, which are used by the electron transport chain”
Wiki. Fatty-acid catabolism involves three stages. The first
stage is
beta-oxidation. The second stage is acetyl CoA oxidation to carbon dioxide. The third stage is electron transfer from electron carriers to
the electron transfer
chain. α-Oxidation is used for branched fatty acids that
cannot directly undergo β-oxidation such as phytanic acid. Fatty acids with very long chains (20
or more carbons) are first broken down to a manageable size in peroxisomes. Nearly every type of
cell can produce its own ATP from fatty acids.
“Muscle cells also contain globules of fat, which are
used for
energy during aerobic exercise. The aerobic energy
systems take longer to produce the ATP and reach peak efficiency, and requires
many more biochemical steps, but produces significantly more ATP than anaerobic
glycolysis, which produces 2 lactic acid molecules” Wiki. Because of the lack
of glycation type
reaction, fats are a preferred ATP source.
Role of dietary fats:
“Knowledge of the nutritional importance of
dietary fats has greatly expanded since the time when fats were considered only
a source of calories. We now know that
dietary fats supply the essential
fatty acids (linoleic and linolenic acid) that are precursors for
prostaglandins and they are important components of membrane structures. Fats
also influence cell functions, serve as
carriers for fat-soluble vitamins, affect immunological function, and are
associated or involved with a number of diseases and disorders” Am
Rev Nut, 1984 pgs.339-364. Though
we have heard much about the importance of the omega-3 fatty acid, saturated
also have important bodily functions.
Reversal on saturated
fats,
history of dogma and its decline: The confusion comes from using
the surrogate marker cholesterol level instead of CVD, though it isn’t a causal
factor.
This is compounded by the association of the artificially high dietary
omega-6 fats (see below section) causes of CVD.
Without a mechanism for the association of CVD
with saturated fats and the failure to find evidence in a meta-analysis of 21
studies,[5] the current government
position on dietary fats (recommending reduction) is in error. “A hundred years ago 1 in 100 obesity
and cardiac heart disease was unknown. The
primary causes of death were enteritis [intestinal infection], TB, pneumonia,
and diarrhea. Heart disease and
cancer today account for 75%
of death. There were 500 cardiologists
practicing in 1950; there are 39,000 now.
In 1911 Procter and Gambled stared marketing manufactured Crisco, which
they marketed it as more healthful than animal fat. It was hydrogenated vegetable
fat. In 1913 Nikolaj Anitschkow (Russian) fed
rabbits cholesterol and showed that it caused atherosclerosis. In 1948 Framingham
Study a comprehensive study of a town in Massachusetts funded by the
government; it showed that those with elevated cholesterol were more likely to
die of heart disease. Six years later
the American Heart Association 6 years later promoted with the prudent
diet. Ancel Keyes Six Country study
found the highest percentage of carbohydrates and the lowest of fats in their
diet have the lowest incidence of heart disease. This study was flawed: Keyes had the data on 22 countries and picked
out 6 to support his hypothesis.[6]
Moreover, those who have the highest saturated fat in their diet have the
lowest rate of coronary disease: Maasi of
Kenya 66% saturated fats; Inuit of Canada, 75%; Rendille tribe of Kenya, 63%;
Tokelau of New Zealand, 63%. Most hunter
gatherers groups eat high amounts of saturated fats, up to 93% of their calories. The
Framingham Study[7]
reversed its position: “(1) over the age
of 50 there is no increased overall mortality form either high or low serum
cholesterol levels, and (2) in people with a falling cholesterol level (over
the first 14 years of the study, before statins) for each 1% mg/dl drop in
cholesterol there was an 11 percent increase in all-cause mortality (over the
next 18 years). Dr. William Castelli,
the third director of the Study, states: “In Framingham, Mass., the more
saturated fat one ate, the more cholesterol one ate, the more calories one ate,
the lower the person’s serum cholesterol… We found that the people who ate the
most cholesterol, ate the most saturated fat, ate the most calories, weighed
the least, and were the most physically active” quoted from the lecture to a
professional audience by Dr. Donald Miller, professor of Surgery at the
Cardiothoracic Division of the University
of Washington, July 17,2011, at http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vRe9z32NZHY. These statements by
Dr. Miller are supported in the journal literature. Dr. Miller also listed on
a slide the
importance of saturated fats:
“Cell membranes:
Require (50%) saturated fatty acids to be waterproof and function
properly.
Heart: Prefers
saturated long-chain 16-carbon
palmitic and 18-C stearic (over carbohydrates) for energy
Bone: needs saturated fats to assimilate
calcium effectively
Liver:
Protects from adverse effects of alcohol and medications like
acetaminophen
Lung: Lung surfactant, which prevent
asthma and other breathing disorders, is composed entirely of 16-C palmitic
acid
Hormones:
Function as signaling messengers for hormone production
Immune system:
Saturated fats play an important role here. They prime white-blood cells
to destroy
invading bacteria, viruses and fungi, and to fight tumors. Medium Chain 12-C
lauric acid and 14-C mystic
acid (in butter) kill bacteria and candida in the gut
Signal satiety:
Promotes satiation through slowing digestion
General health:
Eating saturated fats lowers the consumption of health when compared to
polyunsaturated fats which due to high content of omega-6 fat acids reduce the
positive immune system effect of omega-3 fatty acids.
Reduces age related chronic
conditions which are
a result of the monosaccharides obtained through digestion of carbohydrates which
damage proteins through the process of glycation. Eating less fats entails
replacing them with carbohydrates as a source of energy. The high carbohydrate
Western diet has
brought about the sharp rise in obesity, metabolic syndrome, insulin
resistance, and type-2 diabetes all of which are strongly statistically
associated with an assortment of chronic and fatal conditions.
Saturated fats: Saturated fats were linked to CVD
by failing to control for the transfats, high N-6 to N-3 ratio and
transfats produced through hydrogenation of unsaturated oils. Though these
flaws have been pushed by
business, surprising, 22 metastudies found no association of saturated fats with
CVD.
If you have any
doubt over the venal nature of governments, read about the disjunction between
government holdings around the world, read this footnote. [8] In general, a more reliable way to solve
biological question is in the laboratory where analysis reveals the disease
causing process, and this is confirmed in animal experiments. At Scholar.Goolge.com,
a search of “rats + saturated fats + cardiovascular
disease” had zero studies. Wikipedia also under saturated fats doesn’t have
a section show the bio-pathway for causing CVD.
The proposed association with elevated LDL is without sound, consistent
evidence; moreover, elevated LDL does not promote CVD, though pharma promotes
that myth for to sell cholesterol
lowering drugs—see cholesterol
myth.
The lack of modus operandi based on laboratory experiments is a major
reason to question the putative causal connection to CVD.
A high saturated fats diet
lowers the consumption of sugars and is low in
vegetable oils (lower trans-fats and high levels of n-6), and thus lowers
risk for CVD and obesity. The recommendations of the national health
agencies around the world are another example of marketing before science and
the politicalization of the guideline process.
It stands in contrast to science: A meta-analysis
of 21 studies considered the
effects of saturated fat intake and found that "Intake of saturated fat
was not associated with an increased risk of CHD (coronary heart disease),
stroke, or CVD (cardiovascular disease)” Wiki. Moreover the
main saturated fatty acid from tropical trees (coconut and palm kernel oil),
lauric acid is cardiovascular protective because it increases HDL.[9] Finally “the energy yield from a gram of fatty acids is approximately 9 kcal (37 kJ), compared to 4 k cal/g (17
kJ/g) for carbohydrate,
and compared to carbohydrates fatty acids can hold more than six times the
amount of energy per unit of storage space. Put another way,
if the human body relied on carbohydrates to store energy, then a person would
need to carry 31 kg (67.5 lb) of hydrated
glycogen to have the energy equivalent to 4.5 kg (10 lb) of fat”
Wiki. Fats don’t cause
glycation. For these reasons a diet low
in (a) fructose, (b) those starches that are quickly absorbed (have high
insulin index) and (c) omega-6 and trans-fats, and are high in saturated fats
and most starches is the best source for ATP (energy). Pharma, food industry,
and government have
done it again: turned good into bad, and
the bad into good, and we the consumers pay with the length and quality of our
lives.
Essential fatty acids (EFAs) “are fatty
acids that humans
and other animals must ingest because the body
requires them for good health but cannot synthesize them. Only two fatty acids are known to be
essential for humans: alpha-linolenic acid (an omega-3 fatty acid, N-3) and linoleic
acid (LA, an omega-6 fatty acid, N-6). They
are modified to make. Omega-6 fatty acids are a family of unsaturated fatty
acids that have
in common a final carbon-carbon double
bond in the n-6 position,
that is, the
sixth bond, counting from the methyl end.
Functions (The biological effects of the ω-3 and ω-6 fatty acids are mediated
by their mutual
interactions):
A few
of the polyunsaturated fats in the human
diet are EFAs. Essential fatty acids
play an important role in the life and death of cardiac cells” Wiki. “Following WWI large-scale
production of vegetable oils and the shift to o grain-fed cattle (from grazing
cattle) caused a marked increase in the ratio of the omega 6 to 3 oils from 2:1 to
16:1. Man
evolved in a world for which n-6 to n-3 ratio was around 2:1; the gross 20th
century deviation from this ratio has dire consequences. Proof of this causality
is demonstrated both
in laboratory analysis and clinical trials, but only when the ratio of N-6 to N-3
is 4:1 or less” A.
P. Simopulos. “The actions of the N-3 (omega-3) and N-6 (omega-6) essential fatty acids (EFAs) are best characterized by their interactions; they cannot be
understood separately” Wiki. They
compete for the same receptors during
synthesis, see above. “Some older clinical
studies indicate that the
ingested ratio of omega-6 to omega-3 (especially linoleic vs alpha-linolenic)
fatty acids is important to maintaining cardiovascular health. However, three
studies published in 2005, 2007 and 2008, including a randomized controlled trial, found that, while omega-3
polyunsaturated fatty acids are extremely beneficial in preventing heart
disease in humans, the levels of omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids (and,
therefore, the ratios) did not matter” Wiki.
Omega-3 fatty
acid: “Out of a total of 11, there are three types of omega-3 fatty acids involved in human
physiology are ALA (found in plant oils), EPA, and DHA (both commonly found in marine oils)” Wiki. “Many
experimental
studies have provided evidence that incorporation of alternative fatty acids
into tissues may modify inflammatory and immune reactions and that omega-3 fatty
acids in particular are potent therapeutic
agents for inflammatory diseases [AS, Alzheimer’s, arthritis, etc.] Supplementing
the diet with omega-3 fatty
acids (3.2 g EPA and 2.2 g DHA [N-3s]) in normal subjects increased the EPA
content in neutrophils and monocytes more than sevenfold
without changing the quantities of AA [arachidonic acid] and DHA. Inflammation
plays an important role in both
the initiation of atherosclerosis and the development of atherothrombotic
events. When
humans ingest fish or fish oil, the EPA and
DHA from the diet partially replace the omega-6
fatty acids, especially AA, in the membranes of probably all cells, but
especially in the membranes of platelets, erythrocytes, neutrophils, monocytes,
and liver cells. Inflammation plays an important role in both
the initiation of atherosclerosis and the development of atherothrombotic
events” 2002 Biomed. And again pharma’s devil is in the details of
this 2002 Biomed
article: the negative
results of some studies arise from the failure to limit dietary N-6, which blocks
the positive effects
of the N-3 supplement. The same
is confirmed in Am
J Clin Nutr,
Sept 1999, 560—569 and supported by the reduction in diabetes, arrhythmia,
hypertension, and cardiac arrest.
Another detail is related to source, with vegetable oil derived N-3, ALA;
it has “only about 1/10th the active of EPA and DHA” Wiki.[10] I find the evidence convincing for N-3,
but there are critics: Wikipedia,
e.g., states “but the health benefits of supplementation appear
to be few
if any.” This is
contradicted at Wiki.
Those who challenge the claims for N-3 rely on studies with the principle
source of N-3 coming from vegetable
oil and/or a high ratio of N-6 to N-3;
who’s right?
Omega-6 fatty
acid and CVD: “Excess
omega−6 fatty
acids from vegetables oils interfere with the health benefits of omega−3 fats,
in part because they compete for the same rate-limiting enzymes” Wiki . The disease
promotion effects of N-6 come from
its “conversion to omega-6 eiscosanoids that bind to diverse receptors found in
every tissue of the body…. The eicosanoids from AA [derived from omega 6 linoleic
acid] are biologically active in very small quantities and, if they are formed
in large amounts, they contribute to the
formation of thrombus and atheromas, to allergic and inflammatory disorders,
particularly in susceptible people, and to proliferation of cells
[tumors]. Thus a diet rich in omega-6
fatty acids shift the physiological state to one that is pro-thrombotic and
pro-aggregatory, with increases in blood viscosity, vasospasm, and
vasoconstriction and decreased n bleeding time [promotes ischemic events]. The
higher the ratio of
omega-6/omega-3 fatty acids in platelet phospholipids … caused the higher the
death rate from cardiovascular disease [65,100]. Biomed. Other disease conditions
in this article by A. P. Simopulos for which the evidence from laboratory research,
clinical trials, and epidemiological studies link the unhealthful 16:1 ratio of
N-6 to N-3 to CVD asthma, breast and colon cancers, arthritis and Alzheimer’s
disease. In Paleolithic and
hunter-gatherer times the ratio was 2:1.
N-6 competes with N-3 for
cellular receptors. This attack on omeg-3 follows the pattern of
bad pharma ran by its marketing department which promotes profits first.
Essential fatty acids and arachidonic acid
(AA): “Arachidonic acid (AA) is a 20-carbon
N-6 conditionally essential fatty acid.[1] It sits at
the head of the "arachidonic acid
cascade" – more than 20
different signaling paths that control
a
wide array of bodily functions, but especially those functions involving inflammation and the central nervous system. Most AA in the human body derives from dietary linoleic acid (another essential
fatty acid, 18:2 N-6), which comes both from vegetable oils and animal fats
…. EPA (20:5 N-3) provides the
most important competing
cascade…. These two parallel cascades [second fat is GLA (18:3 N-6)] soften the inflammatory effects of AA and its products. Animal studies show that increased dietary N-3
results in decreased AA in brain and other tissues. The reverse is also true –
high dietary linoleic acid decreases the body's conversion of α-linolenic acid
to EPA. Low dietary intake of these
less inflammatory essential fatty acids,
especially the N-3s, is associated with a variety of inflammation-related
diseases…. These changes have been accompanied by increased rates of many
diseases – the so-called diseases of civilization – that
involve
inflammatory processes. There is now very
strong evidence that several of these diseases are
ameliorated by increasing dietary N-3, and good evidence for many others.
There is also more preliminary evidence showing that dietary N-3 can ease symptoms
in several psychiatric disorders” Wiki. The totality of
evidence support dietary changes with reduced N-6 and N-3 supplementation.
So what is driving this high ratio: Among the changes
have been the effects of grain fed livestock and chicken. For example USDA eggs
have a ratio of 20 to
1, while Amplelistra farms in Greece the ratio is 3 to 1.3, 2002 in Biomed. Other sources rich
in N-6 include vegetable oils and
nuts. On these grounds it is a good
course to increase intake of fish over meats[11]
and limit vegetable oils and nuts. Based
on the totality of evidence, a prudent course is to lower the ratio of N-6 to
N-3 both by changes in diet and taking fish oil pills high in N-3, which can be
obtain quite economically from Costco.
Thus to maximize benefits limit n-6.
Health benefits of Omega-3:
The American Heart Association in a 2003 on intake
of omega-3
made finds and issued
recommendations.
“Research to date suggests that they {omega-3] can decrease risk for
arrhythmia, thrombosis, triglyceride and lipoprotein levels, rate of growth of
growth of the atherosclerotic plaque, improve endothelial function [arteries],
(slightly) lower blood pressure, and inflammatory responses. The AHA
recommends that all adults eat fish (particularly fatty
fish) at least two times a week. For
patients with documented CHD, the AHA recommends ≈1 g of EPA and DHA (combined)
per day. … An EPA+DHA supplement may be useful in patients with
hypertriglyceridemia. Two to four grams of EPA+DHA per
day can lower
triglyceride 20% to 40%.
100 gm portions in gm,
omega 3 & 6 fatty acids, omega-3
listed first (blank when under ½ gm http://nutritiondata.self.com/tools/nutrient-search (a
user friendly resource)
|
Safflower oil
- 75
|
Walnuts
9.0 38
|
Canola Oil
7.6 19
|
|
Sunflower oil 0.9
66
|
Bread
shortening - 37
|
Potato chips - 16
|
|
Commodity food
oil 7.0 50
|
Margarine hard
- 36
|
Peanuts raw - 15
|
|
Corn oil
1.1 53
|
French fries
- 13
|
Pistachio
- 13
|
|
Mayonnaise 3.0 52
|
Shortening
vegetable 4.7
26
|
Lard
1.0 10
|
|
Soy oil
6.7
50
|
Pecans
1.0 20
|
Salmon oil
35 01.5
|
|
Salmon baked 4.0 1.2
|
Chicken fat
1.0 19
|
Butter
1.1 02.7
|
Plant
sources of N-3 are mostly ALA, of which about only
1/10th is converted to the essential EPA and DHA. Another source
on content of oils is at eat
real food site.
Fishes high in
Omega-3 p er
85 gm serving in grams: herring &
sardines 1.3-2, mackerel 1.1-1.7, salmon 1.1-1.9, halibut 0.60-1.12, tuna
0.21-1.1, swordfish 0.97, shark 0.84, flounder 0,48
Fatty
Acids in Dietary Fats -- Wiki
[2]
Glycation is a type of oxidation in which a monosaccharide--most often glucose
or fructose—attaches to a unsaturated fat molecule. Fructose is 7 times
more reactive than
glucose and serum level remain higher longer.
[3]
The recommended average intake of omega-3 for adult men in the
United States is only 1.6 grams/day, or less than 2% of total fat; the actual
average consumption of omega-3 in the United States is around 1.3 grams/day,
almost all of it in the form of ALA; [of which under 10% is converted to EPA
and DHA the healthful forms] EPA and DHA contributed less than 0.1 grams/day” Wiki .
[4]
High dietary level of N-6 blocks the
conversion of N-3 and thus it
healthful effects, and as a consequence N-6
is causal for CVD.
[5] A meta-analysis of 21 studies considered the effects of saturated
fat
intake and found that "Intake of saturated fat was not associated with an
increased risk of CHD (coronary heart disease), stroke, or CVD (cardiovascular
disease)” Wiki.
[6] It
was later exposed that he had received funding from the food industry.
[7]
The Framingham
Heart Study is a long-term,
ongoing cardiovascular study on residents of the town of Framingham, Massachusetts.
The study began in 1948 with 5,209 adult subjects from Framingham, and
is now on its third generation of participants.
Prior to it almost nothing was known about the "epidemiology of
hypertensive or arteriosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Much of the now-common
knowledge concerning
heart disease, such as the effects of diet, exercise,
and common medications such as aspirin,
is based on this longitudinal
study.
It is a project of the National
Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute,
in collaboration with (since 1971) Boston
University.
Over 1000 medical papers have been published
related to the Framingham Heart Study. It is generally accepted that the work
is outstanding in its scope and duration, and overall is considered very
useful. showed the importance of healthy
diet,
not being overweight or obese,
and regular exercise in maintaining good health, and that there are
differences in cardiovascular risk between men and women.[9][10] It also confirmed that cigarette smoking is a highly significant factor in the
development of heart disease, leading to angina
pectoris, myocardial
infarction (MI), and coronary
death,.
Framingham Risk Score is published, and predicts 10-year risk
of future coronary heart disease (CHD) events. Recently the Framingham studies have
become regarded as overestimating risk.
On the web at http://www.framinghamheartstudy.org/
[8] Leading medical, heart-health, and
governmental authorities, such as the World Health Organization,[16] the American Dietetic
Association,[17] the Dietitians of Canada,[17] the British Dietetic
Association,[18] American Heart
Association,[19] the Indian Heart Association,[20] the British Heart Foundation,[21] the World Heart Federation,[22] the British National Health
Service,[23] the United States Food and Drug Administration,[24] and the European Food Safety
Authority[25] advise that saturated
fat is a risk
factor forcardiovascular
disease (CVD). A number of systematic reviews have examined the relationship
between saturated fat and
cardiovascular disease and have come to different conclusions” Wiki.
[9] “Lauric acid increases total serum cholesterol the most of any fatty acid. But most of
the increase is attributable to an increase in high-density lipoprotein (HDL) (the "good" blood cholesterol).
As a result, lauric acid has been characterized as having "a more
favorable effect on total HDL cholesterol than any other fatty acid, either
saturated or unsaturated” Wiki.
[10] Consumption of
omega-3 in the United
States is around 1.3 grams/day, almost
all of it in
the form of ALA.. ALA can be partially
converted into EPA and DHA by the
human body, but the conversion
rate is thought to be 10% or less, depending on diet and gender” Wiki .
[11]
Another reasons to substitute fish for meats and poultry is the use of
plant manufactured pesticide in the grains fed cattle. There is strong
evidence for serious health
consequences from corn and eating corn and soya fed animals (thank you
Monsanto).
|
 |
|
Polyunsaturated fats
are subject to rancidification: “is the hydrolysis and/or autoxidation of fats into short-chain aldehydes and ketones which are objectionable in taste and odor. Hydrolytic rancidity refers to the odor that develops when triglycerides are
hydrolyzed and free fatty acids are released to form free
tatty acids and salts of free fatty acids.
Oxidation primarily occurs with unsaturated fats. Microbial rancidity refers to a process in which microorganisms,
such
as bacteria or molds, use their enzymes such as lipases to break down fat.[1] Rancidification can produce
potentially toxic compounds
associated with long-term harmful health effects concerning advanced aging,
neurological disorders, heart disease, and cancer. A combination of
water-soluble and fat-soluble antioxidants is ideal” Wiki. A key
source for oxidized fats comes from
frying and deep frying. The alarm
was
raised in work done at Rutgers University in 1978, where a team in a simulation
of commercial frying where they tested commonly used polyunsaturated in
simulated deep frying at 365° F for 74 hours. One finding,
for example was that “under such
conditions [of commercial frying] both thermal and oxidative decomposition of
the oil may take place. Such unavoidable
chemical reactions cause formation of both volatile and nonvolatile
decomposition products…. Various symptoms of toxicity, including irritation of
the digestive tract, organ enlargement, growth depression, and even death have
been observed when highly abused (oxidized and heated) fats were fed to
laboratory animals”… and the article goes on. “Lipid
peroxidation refers to the oxidative
degradation of lipids. It is the process in which free radicals "steal" electrons from the
lipids in cell membranes, resulting in cell damage. It most often affects polyunsaturated fatty acids, because they contain multiple double
bonds in between which lie methylene bridges (-CH2-) that possess especially reactive hydrogens.
If not terminated fast enough, there will be damage to the cell membrane, which consists mainly

of
lipids. In addition, end-products of lipid peroxidation
may be mutagenic and carcinogenic. For
instance, the end-product malondialdehyde reacts
with deoxyadenosine and deoxyguanosine in DNA, forming DNA adducts to them, primarily M1G”
Wiki.
The detailed 2010
article
Pathological Aspects of Lipid Peroxidation list aging, Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease,
amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS, Lou Gehrig’s disease), atherosclerosis (and
thus CVD and
other related
conditions), pre-eclampsia (pregnancy disorder affecting about 4%), diabetes,
renal diseases, chronic lymphedema
(also
known as lymphatic obstruction, causing swelling by compromised lymphatic
system), hepatic diseases including liver IR,
NAFLD, NASH (#16), exacerbating
hepatitis C and cirrhosis of the liver, and a causal factor for cancers. The various authors of each section of this
in-depth article describe the process by which the lipid peroxidation causes pathology. The role of oxidation of fats and cholesterol
within the artery walls as being atherogenic is clearly made in that
article. The effects of rancidification
in the body are beyond dispute. Also
contributing are dietary sources of rancid oils.
“The
possibility that the body fats might undergo a similar kind of degradation is
still largely ignored—perhaps
because the irregular irreversible pattern of this type of process seems at
odds with the enzyme-controlled reversible pathways of traditional biochemistry.
Yet work with mitochondria and other biological preparations has shown that the
processes commonly grouped together as " degeneration ", "
fatigue ", and " ageing " (none of which have a basis in
classical enzymology) develop in close parallel with evidence of Rancidification”
at 1969.
The source can either be dietary rancid fats
or in vivo oxidation—in vivo causing the greatest issues.
Now let us follow the chain of events
concerning IR and CVD.
Rancid fats contribute to liver dysfunction NAFLD and IR by
accumulating in the liver in a form that the liver can’t dispose of.
Similarly they contribute to atherosclerosis
and CVD by being in a form with the
muscle cells in the tunica media (muscular layer) of the artery walls which
prevent uptake for transport and metabolized.
The macrophages in the tunica media similarly can’t dispose of the
rancid fats. Thus like transfats
(see
section below) rancid fats contribute to CVD
and atherosclerosis. “Accumulating
evidence suggests that oxidized fats and lipid
oxidation products in the diet can contribute to the pathogenesis of
atherosclerosis” at 2002, and 1998. Non-enzymatic oxidation causes the failure of
the body to dispose of them; they accumulate like those of the unnatural,
man-made trans-fats. Thus
polyunsaturated fats are unhealthful because of rancidification and because of
their high N-6 content. Like other vegetable
with low yield through expeller-press
undergoes a complex process involving organic solvents, distillation to remove
the non-oil fraction, treatment with alkali to neutralize free fatty acids,
bleaching to remove modify color, and distillation at a temperature of 480° F and under a
high vacuum.
Corn oil has 55% polyunsaturated fat, Cottonseed 52%, canola 28%,[2]
soybean 58%. Moreover as stated
above
rancidification in the body and the high amount of omega-6 makes this and all
oils high in unsaturated fats a major health concern. Corn oils ratio of n-6 to n-3 is 49:1.[3] (See section on n-6 and n-3 above).
So what does our corporate friendly
government do?
Commercial forces behind vegetable
oil: For
example, corn oil is derived from the waste part, the germ, of corn in the
production of corn meal used in animal feed and various grocery foods.
Being a waste byproduct of a commercially
valuable product makes it is “generally less expensive than most
other types of vegetable oils. One
bushel of corn contains 1.55 pounds of corn
oil (2.8% by weight) [and a lot of animal feed]. Corn
oil is also a feedstock used for biodiesel. Other industrial uses for corn oil
include soap, salve, paint, rustproofing for metal surfaces, inks, textiles, nitroglycerin, and insecticides. It is sometimes used as a carrier for
drug molecules in pharmaceutical preparations” Wiki. Being
cheap it is favored by the food manufacturers.
To promote manufactured food sales they have influenced government to
subsidized crops, to recommend a low fat diet (thus high carbs), and to vilify
saturated fats as artery clogging to promote their cheap polyunsaturated fats
as heart healthy. Over 95% of
Federal-farm crop subsidies go to the production of grains. The cheap subsidized grains have made it
possible for the food manufacturers to sell their products abroad.
As developed in the article on diet, the
global obesity & diabetes pandemics are founded upon sugar added
manufactured foods combined with a diet high in grains (a one-two-punch)--see. And
it get worse since baked products which
use a high ratio of polyunsaturated fats are clearly inferior in flavor, the
food manufacturers hydrogenate them (a cheap process) to convert them to
superior baking properties of saturated fats.
In this process about half of the polyunsaturated are converted to the
equally unhealthy transfats—section below. The transposition is lower energy, and thus
favored, in catalytic hydrogenation. Thus
what is sold as heart healthy; isn’t; and what is artery clogging turns out to
be healthy, viz., the best source for energy (ATP). This is an example of what I call tobacco
ethics and tobacco science: corporations
pursing the corporate imperative of maximizing profits.
Trans-fats:
“The daily intake of about 5 g of trans
fat is associated with a 25 percent increase in the risk of ischemic heart
disease”
NEJM. However, this study was based on the use of questionnaire
given
667 elderly 3 times over 10 years—hardly proof, at. “Trans-fats
are
found only in trace amounts in meat and dairy products. Their major source is in food
production: liquid cis-unsaturated
fats such as vegetable oils are hydrogenated to produce saturated
fats, which have more desirable physical properties[4] [and more flavorful baked
and fried foods]. Trans-fats are a contaminant introduced by a side
reaction on the catalyst in partial hydrogenation of vegetable oils.
However, partial hydrogenation reconfigures
most of the double bonds that do not become chemically saturated, twisting them
so that the hydrogen atoms end up on different sides of the chain. This type of
configuration is called trans, from the Latin, meaning "across".[39] The trans
configuration is the lower energy form, and is favored when catalytically
equilibrated as a side reaction in hydrogenation” Wiki. Another study found
a 30% increase—2015
BMJ. In 1975, 5.6
billion Ib. of hydrogenated vegetable oil were produced in the United States,
which is an average of 28 Ib/year/person (113)” ARN, 1984. Based on population studies and clinical trials,
trans-fats are blamed for high levels of cholesterol, lower the good HDL, and
as a major cause of CVD. But as pointed out in the section on the
Mediterranean diet, complex population studies are like data mining, where you
dig determines what you find, and sometimes proposed mechanism and population
data is only poorly related to CVD. However, animal study using Wistar rats found
that transfats in a high fat diet causes fatty liver disease at 2011. However,
the
study which found oxidation didn’t control for the effects of polyunsaturated
fats which are subject to rancidification (see poly section below).
Another study found the same in transfats and
high-fructose corn syrup—at 2008. By promoting
metabolic dysfunction, we have
the mechanism, like that of T2D for
transfats, and presumable polyunsaturated fats as to their method of causing CVD.
Is there laboratory evidence
that trans-fats cause CVD? Back
to the cholesterol myth: “trans-fats
increases the risk of coronary heart
disease by raising levels of the lipoprotein LDL (so-called
"bad cholesterol") and lowering levels of the lipoprotein HDL ("good
cholesterol") “ Wiki. “It is now well known that the
hydrogenation process and particularly the formation of trans-fatty acids has
led to increases in serum cholesterol concentrations whereas LA [linoleic acid]
in its regular state in oil is associated with a reduced serum cholesterol
concentration” Biomed. This has been confirmed with high trans-fat in clinical
experiment on volunteers. But it has been shown (see part 2) that pharma pushes the high LDL,
high TC, and high-fat diet as causes of CVD for to promote drug sales; they are not causal factors, rather it promotes sales of statins. The cause of CVD from a 2006 review article on trans-fats besides changes in LDL and HDL:
“Because of their effects
on the metabolism of gamma-linoleic and arachidonic acid,
ingestion of trans-fatty acids can affect the metabolism of prostaglandin and
other eicosanoids and may alter platelet aggregation and vascular function
[negative effect upon inflammation (causal of AS) and clotting functions (causal of MI)]. In addition incorporation of trans-isomers
into membrane phosopholipids may influence the physical properties of the
membrane as well as the activities of the membrane-associated enzymes …. Effect
collagen induce platelet aggregation.… inhibit activities of Na+
, K+-ATPase
and adenylate cyclase and reduce density of B-adrenergic receptors in rat heart
membranes [raise blood pressure]…. Recent evidence indicates that trans-fats promote inflammation…. Increased tumor
necrosis factor (TNF) system, levels of interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein….
Several studies suggest that trans-fats cause endothelial dysfunction [affects
wall of arteries and other tissues]… soluble vascular-cell adhesion
factor…reflected by reduction
in
brachial artery flow-mediated vasodilation by 29 percent [raises blood
pressure], as compared with intake of saturated-fats. Other effects include consumption of
trans-fats reduced the activity of serum paroxonase, an enzyme that is closely
associated with HDL cholesterol, and impaired the postprandial activity of
tissue plasminogen activator. Trans-fats
appear to affect lipid metabolism through several pathways….”
The same finding with much greater detail is
in the 1984 thorough review by the Department of Agriculture. Several epidemiological studies found a significant
association of trans-fats with CDV
and MI, including those studies
which controlled for contravening variables.[5] As previously stated
LDL and high TC are again bystanders,
and trans-fats
affects some of the same processes as omega 6.
Given the clear association in dozens of population studies and clinical
trials of trans-fats to CVD, governments have responded to this health hazard
created by the food industry. With
the
body of experimentation upon rats a mechanism for the deleterious effects of trans-fats
has been established, the principle one being it effect upon blocking the
conversion of the essential omega-3 fatty acid, at. The smoking
gun
lines with the fact that trans-fats exert a pro-inflammatory effect, and the
inflammatory processes in artery walls in response to damaged LDL causes
atherogenesis. “Because the
presence of
inflammation is an independent risk factor for atherosclerosis… the production
of interleukin-6 and TNF-a by cultured mononuclear cells was grater
after one month…” NEJM—see also, a 2006 summary article.
Laboratory experiments on rats are revealing.
Strong association with NAFLD, obesity, and MeS
are associated in rats with a diet high in trans-fat. “By 16 weeks, trans fat-fed mice became obese
and developed severe hepatic steatosis with associated necroinflammatory
changes… severe hepatic steatosis… glucose intolerance developed within 2 and 4
weeks… plasma insulin resistance… Because dietary
transfats promoted liver steatosis and injury, their role in the epidemic of
NASH needs further evaluation” at 2008, and like findings 2011. This is an extremely important health
finding, the causal change to obesity risk and MeS and T2D starts with
accumulation of fat within the liver, which mucks up the liver’s metabolic
regulatory function. Now in addition to
fructose with a high starch diet, we can add unhealthful trans and
polyunsaturated fats. The omega-6, transfats are
pro-inflammatory because of the inhibition of on EFA metabolism, 1984. This effect
on n-6 is associated with heart disease
in
rats on trans-fats--1997 . It thus
based on
lab and population studies to assiduously avoid artificially produced
trans-fats[6]. The zero trans fats on food label is
deceptive for 2 reasons, at 0.5 grams the entry is 0, and since no one is
checking food content, there is an incentive to manufacture numbers on product
labels.
What
are the regulations:
Official response has been prohibiting trans-fats in a number of
countries, but not the U.S. “According to the FDA, the average American consumes
5.8 grams of trans-fat per day (2.6% of energy intake). This is government
figure is low because trans
fatty acids that are part of mono- and diglycerides [bound with glycerol] are
not required to be listed on the ingredients label as making contributions to
calorie count or trans fatty acid content.
Trans-fats in the form of
monoglycerides and diglycerides are not considered fats by the FDA, though upon
absorption from digestive track they yield trans-fats. Another gap in calculation
is that trans-fat
levels of less than 0.5 grams per serving are listed as 0 grams
trans-fat on the food label. There
is no requirement to list trans-fats
on institutional food packaging; thus bulk purchasers such as schools,
hospitals, [restaurants] and cafeterias
are unable to evaluate the trans-fat content of commercial food items [nor
is there an incentive to spend more for trans-free foods]” Wiki. The
major source of trans-fats in the U.S. is
in fried foods from restaurants, and this source is not included in US
dietary figures for trans-fats. A number of countries have
simplified the process of controlling trans-fatty acids by banning them, starting with Denmark in 2003 and
now also Iceland, Sweden, Switzerland .
“Spain … no significant levels of trans-fats were found in any of the
anaylsed products, regardless of brand of origin” at Bakery. The regulations might
make a difference, because death rate per 100,000 2011 from coronary heart
disease is 80.5 US, 55.9 for
Denmark, for Spain 43, Switzerland 52 ,Japan 31, Israel 46, Italy 51, Greece
60, U.K. 69, and France 29, source LeDuc Media. However, the
highest rate of obesity and diabetes is in the US, and the US allows GMOs. Let us not become
distracted by what could by the minor causes such as fats when the elephant in
the kitchen are refined carbs and
sugars. The weakness of lab work
on fats make the case,[7]
we need to look at the Western high carb diet.
The
Western diet:
Avoid the western diet and avoid fructose, trans-fats, and high ratio of
n-6 to n-3 and fats subject to rancidification
(main source vegetable oil), but not starches, saturated fats, and
polyunsaturated fats low in n-6. Note,
since the process of AS is initiated by NAFLD
mucking upon metabolic regulations which starts with the
combination of high fructose and high insulin caused by carbs, avoid the Western
diet. Thus instead of high fat diet and
high levels of cholesterol being the chief villains in the life ending CVD, it
is the Western diet with
large amount of fructose, sucrose, refined
carbs,[8] tobacco smoke, and polyunsaturated and transfats that has caused
most
of the spike in CVD and varied health
problems facing the elderly, especially
those involving oxidative damage and immune responses (arthritis, Alzheimer’s
& Parkinson’s
diseases, macular degeneration, CVD,
and insulin resistant diabetes). Place
sugars as first, refined carbs second, and vegetable oils third on the dietary
avoid list—the carbs connection see part
4.
Why the Mediterranean
diet works:
“The recently published PREDIMED randomised controlled trial
was stopped early after it showed that in high risk people the Mediterranean
diet achieved a 30% improvement over a “low fat” diet in terms of
cardiovascular events” BMJ.
There is major variation
between
regions of the Mediterranean. Wikipedia concludes:
“The all-embracing term 'Mediterranean diet'
should not be used in scientific literature.” Among errors:
“olive oil consumption is negligible…
Mediterranean countries tend to consume relatively high amounts of fat, they
have far lower rates of cardiovascular
disease than in countries like the United States,
where similar levels of fat consumption are found…The most popular
dietary candidate, olive oil, has been undermined by a body of experimental
evidence that diets enriched in monounsaturated fats such as olive oil are not
athero-protective when compared to diets enriched in either polyunsaturated or
even saturated fats. A healthy active lifestyle (notable a physically
active lifestyle or larbour) is also beneficial… red wine … contains flavonoids with powerful antioxidant properties… The
proposed mechanism is solar UVB-induced synthesis [sun] of Vitamin D in the
oils of the skin, which has been observed to reduce the incidence of coronary
heart disease, and which rapidly diminishes with increasing latitude…. A recent randomized Spanish trial of diet
pattern published in The New England
Journal of Medicine in 2013 followed
almost 7,500 individuals over around 5 years found that individuals on a
Mediterranean diet supplemented with mixed nuts and olive oil had a 30 percent
reduction in risk of having a major cardiovascular event and a 49 percent
decrease in stroke risk. A 10-year study
found that adherence to a Mediterranean diet and healthful lifestyle was
associated with more than a 50% lowering
of early death rates” Wiki.
Undoubted influenced by pharma’s thought
leaders, the Wikipedia article basically a survey, a kitchen sink without clear
guidance & no mention of sucrose, fructose, refined carbs, or
glycation. However the research
in this
series on CVD place as beneficial
low
use of sucrose first, refined carbs second, followed by saturated fats and
monounsaturated fats, then physical active life style and the lower use of
pharma’s patented drugs as why those on a Mediterranean diet live longer. Moreover the first study of this diet started
in the 50’s based upon Italians who ate a peasant diet. [9]
Other factors include lower rate of obesity, popularity of red wine (its
anti-oxidants), effective regulation of trans-fats (unlike the US), and higher
intake of diary product with its vitamin D and sunlight (this combination of
calcium, vitamin D, and sun light is cardio-protective). Wikipedia’s article on the Mediterranean diet
repeats the tobacco science of the food and pharmaceutical industries.
Human
evolved a biological system for the
hunter-gatherer life, not the modern diet.
1871
census UK and
longevity: More evidence of the consequences of
the western diet: the 1871
census in the UK (the first of its kind) found the
average male life expectancy as being 44, but if childhood mortality is
subtracted, “males who lived to
adulthood averaged 75 years. The present male life expectancy in
the UK is 77 years for males [the United States averages 74 for males]” Wiki. In spite of
the
improved medical procedures[10]
for cancer, heart attacks, strokes, vaccinations preventing contagious
diseases, and antibiotic to treat infections,[11]
and also a safer work environment, these benefits have been undone as to life extension
by CVD, cancer, osteoporosis,
Alzheimer’s disease, for which
western diet and lifestyle are the major causes.
Fats, what’s good; what’ s bad: Omega-3
fatty acids (N-3) EPA and DHA are converted in the body to essential products that modify
inflammatory and immune reactions and thus N-3
lowers the risk of autoimmune diseases including Alzheimer’s, arthritis, and CVD.
Omega-6 fatty acids (N-6) have
an inflammatory effect and also block the conversion of N-3
and thereby increase autoimmune diseases including AS and CVD.
The ideal ratio of N-6 to N-3
is 4:1 or less; the western-diet ratio is 16:1. Main source for N-6 are vegetable oils and nuts.
Canola oil[12]
is the
only major vegetable oil with a good ratio of N-6 to N-3
(2.5:1), although the main omega-3 is the form of
alpha-linolenic acid of which only about 10% is converted to the healthful EPA and DHA. Because Canola oil is from GMO canola, I must withhold recommending
it;[13]
most other
vegetable oils are from GMO crops. Main
source for EPA and DHA is fish oil supplement and
fish. For vegetable oils to avoid N-6, the best
are coconut, palm, and olive oils and they are free of GMO. However, I must withhold recommending olive
oil; its N-6 to N-3 ratio is 14:1. Another
issue for vegetable oils is that of rancidification which makes them comparable
to that of transfats. Our
body’s lack
enzymes for their metabolism, and thus insufficient amounts they accumulate in
our cells and causals for an assortment of conditions including CVD.
Moreover most vegetable oils come from GMO seeds which are not only
Roundup read but also have a GMO pesticide that causes leaky gut.
Because leaky gut kills insects, there is a
major human risk.[14] The
switch to grain fed poultry and cattle
from free range has lowered the amount of N-3
in those meat sources. In
manufactured
foods and restaurants trans-fats are a concern.
They are a result of partial hydrogenation of vegetable oils. While banned in many developed countries,
U.S. regulations require only listing trans-fat content on label.
However, there are several exclusions in the
regulations, and those labels are based on the corporate honor system without
government oversight. Secondly,
restaurant and institutions are excluded from regulations, thus their baked and
fried foods are another major source. Trans and saturated fats enhance the
flavor of baked goods and fried foods. Trans-fats promote CVD and other autoimmune
diseases. The palm nut[15]
are high in saturated fats including the beneficial lauric
acid and thus are recommended along with
animal sources of saturated fats, and also monounsaturated fats. After them comes olive oil with its low level
of polyunsaturated fats. Thus
as a
policy, limit vegetable oils, commercial backed goods, and restaurant baked
deserts and fried foods. Animal
fats
because of the GMO plant pesticide and Roundup issues, I thus withhold
recommending lard.[16] Substitute
saturated fats such as butter and
vegetable oil from palm tree nuts, eat more seafood, and take omega-3
supplement. “If
insulin is elevated there is a net inward flux of FFA [free
fatty acids], and only when insulin is low can FFA leave adipose tissue.
Insulin secretion is stimulated by high blood sugar, which results from
consuming carbohydrates” Wiki. Thus a low
carbohydrate
diet with saturated fats replacing them and sea foods is recommended for weight
control and lowering CVD risk. A
more complete accounting of what
constitutes are good diet is found at Diet recommendations
and its science which is a short
non-technical summation followed by diet recommendations and at Healthful
lifestyle which has also a
list of several healthful drugs that pharma of course opposes.

^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
[1]
This affect by bacteria is one of the causes for atherosclerosis. Bacteria are found in the tunica media
(muscle of artery walls) and are a major cause for CVD. Another example of pharma distorting the beliefs about CVD—for confirmation of infectious agent role.
Thus the toxins from bacteria damage both the
LDL and its fatty acid content.
[2]
Don’t assume that canola is better, because like corn, soy, it has a GMO gene
and thus makes its own pesticide and another making it Roundup read, meaning
that the crop is probably dosed in that herbicide.
[3] “Some medical research
suggests that excessive levels of omega-6 fatty acids, relative to omega-3 fatty acids, may increase the probability of a number of
diseases and depression.[7][8][9] Modern Western diets typically have ratios of
omega-6 to omega-3 in excess of 10 to 1, some as high as 30 to 1, partly due to
corn oil which has an omega-6 to omega-3 ratio of 49:1. The optimal ratio is
thought to be 4 to 1 or lower”[10][11] Wiki.
[4] Desirable properties of not
being subject to oxidation (they lack a double bond unsaturated fats), which
improves flavor, and they “melt at a desirable temperature (30-40°
C)” Wiki.
Removing trans-fats following hydrogenation of vegetable oil adds to its
cost. Thus
for flavor, shelf-life, and
price hydrogenated vegetable oils are commercially valued.
[5] A well designed
study in Boston looked
at the dietary intake of 239 hospital patients with their first MI were matched
to 282 control subjects. A questionnaire
was used to estimate dietary intake of trans-fats, and adjustments were made
for contravening variable. “Relative
risk for the highest quintile, 2.44.”
Trans-fats constituted 1.6% of daily energy intake. The highest quintiles consumed twice
the
daily intake of the lowest. “The
association could not be explained by other established risk factors.”
[6]
Trans-isomers of fatty acids constitute about 5% to 6% of dietary fat in the
average US diet, mostly derived from partial hydrogenation of vegetable oils….
Typical margarines in the US market range
from 10% to 30% of total fat… more than 10% of total fat are also frequent in
cookies, crackers, breads, pastries, and French-fried potatoes” at AHA.
[7]
There are just two studies using a Google Scholar search of the
literature. One population wing of the Nurses’
Health Study found a clear association after controlling for confounding
variables of transfats with CHD
(coronary heart disease). The other was trial using rats of 4
cohorts (6 in each): trans-fat +
HFCS, lard + HFCS, trans-fat, and control (without forced sedentary lifestyle). The combo of HFCS and trans-fat had had the
greatest weight gain, and liver weight gain, but there was no indication as the
CHD
(possible by deliberate
omission). Liver damage is not a proven surrogate for CHD. The lack of an animal study is telling.
[8]
True dietary fat raises LDL, but it’s the large buoyant kind. The small desne variation is raised by
carbohydrates.
[9] The village of Pioppi and surrounding area
(south of Naples) the source for data on the Mediterranean diet in the 50s. at.
[10]
Joseph Lister sterile
procedures were first applied on a limited scale in 1869 during operations and
treating wounds, and not widely for at least a decade. Moreover, there weren’t antibiotics. Most contagious diseases such as
tuberculosis, bronchitis, syphilis and cholera lacked effective treatments, and
there were only a few prevented by inoculation.
[11] Don’t assume that we have
a
large arsenal of wonder drugs. After carefully examining the evidence on most
of the drug treatments such as for arrhythmia, hypercholesterolemia, dementia,
hypertension, cancer, arthritis, osteoporosis, COPD, and psychological
conditions, I have come to agree
with a French book by two noted doctors, that over
half are not worth their side effects, and in particular for those conditions
just named. What we and are physicians are fed is pure marketing and thus
always distorted. With pharma’s regulatory capture and the control of medical
education through KOLs, we have revisited the past, before the golden age of
medicine. I have dedicated this
website
and my retirement years to investigating and publishing the best evidence based
conclusions on bad pharma and bad diet.
What we get is a product of the corporate imperative to maximize profits. To give the
process an historical connotation
I call it “tobacco science” and “tobacco ethics”. On the positive side I have investigated some of the drugs
which such as sex hormones and aspirin, which pharma warns us about as
dangerous, though once they demonstrated as healthful.
Similarly I have looked into diet, and again
found more tobacco ethics.
[12] “Canola oil is produced
from the
seed of any of several varieties of rape plant namely a cultivar of either rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) or field mustard/turnip rape (Brassica rapa subsp. oleifera,
syn. Brassica campestris L.). Consumption of the oil is common and does
not cause harm in humans and livestock. Canola
was bred naturally from rapeseed at the University of
Manitoba, Canada…
in the early 1970s. The "Can" part stands
for Canada and "ola"
refers to oil. The breed rapeseed at University of Manitoba had a very
different nutritional profile in addition to much less erucic acid.
Annual Canadian exports total 3 to 4 million tonnes of the seed, 800,000 tonnes of canola oil,
and 1 million tonnes of canola meal. Within the United States, 90% of the
canola crop is grown in North Dakota.
The rapeseed blossom is a major source of
nectar for honeybees. In the 2010–2011 season, world
production of canola oil is estimated to be at 58.4 million tonnes. Approximately
43% of a seed is oil.[24] What remains is a rapeseed meal that is used as
high quality animal feed. 22.68 kg (50 lb) of
rapeseed makes approximately 10 L (2.64 US gal) of canola oil.
Canola oil is a key ingredient in many foods. Its reputation as a healthy oil
has created high demand in markets around the world, and overall it is the
third most widely consumed vegetable oil in the world” Wiki.
[13] “A genetically
engineered rapeseed that is
tolerant to herbicide was first introduced to Canada in 1995 (see Roundup Ready Canola). In 2009, 90% of the Canadian crop was
herbicide-tolerant. As of 2005, 87% of
the canola grown in the US was genetically modified” Wiki. “To produce the Roundup Ready canola, two
genes were introduced into the canola genome. One is a gene derived from the
common soil bacterium Agrobacterium strain CP4, that encodes for the EPSPS enzyme. The
other is a gene from
the Ochrobactrum
anthropi strain LBAA, which
encodes for the enzyme glyphosate oxidase(GOX)” Wiki. The government safety regulatory
process is
a total façade, and studies on safety are influenced by Monsanto—Genetic
Roulette.
[14] How much the risk is difficult
to solve, because industry funds most of the studies. I have yet to view the literature, but the
movie Genetic
Roulette sounds a very believable warning.
[15] Coconut oil and palm kernel oil
is about 85% saturated fats while palm oil is only 48% saturated fats.
[16] As for butter, the bovine
hormone should not be an issue for humans since it must be injected; viz., it
is not orally active. It is the
corn
feed, and possible other grains which have a plant produced pesticide that is
the issue. I also suspect that using GMO grains in feed would not affect the
organic rating of meat products, for the certification system is broken, for it
is done by corporations without meaningful government oversight.
|
 |
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
Enter supporting content here
INTERNAL SITE SEARCH ENGINE by Google
|
|
|
|
 |