|
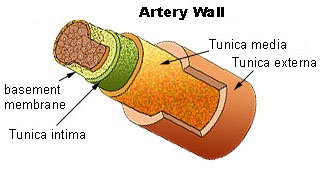
Artery
basics: Endothelial
Cells (ECs): “In a healthy vascular system the endothelium lines all blood-contacting surfaces, including
arterioles, arteries, veins, capillaries, and heart chambers” Wiki. “Endothelial Dysfunction[1](ED) is
a major physiopathological mechanism that leads towards coronary artery disease, and other atherosclerotic diseases” Wiki. While the
illustrations and literature is on ED of the coronary arteries for CVD and the
other arteries for atherosclerosis, a key role is played by the ECs in the
blood vessels that nourishes the 3 layers of artery. “The vasa
vasorum (Latin, "the
vessels of the vessels") is a network of small blood vessels that supply the walls of large blood
vessels, such as elastic arteries (aorta) and large veins (vena cava).… In
smaller vessels it penetrates only the outer layer” Wiki. The main coronary arteries are sufficiently large as to require
a network of blood vessels for oxygen, the vasa vasorum.
Cardiovascular
disease (CVD): Thus far I have shown
that pharma’s hypothesis as to the
cause of CVD is not merely a minor
causal factor, but totally
false (the cholesterol-saturated fats myth). I have answered the question what causes CVD by showing that pathogens and the
subsequent immune response (including
LDL mopping up bacterial toxins) play the key role in
the
development of atherosclerosis. This
still leaves the question of how does
the Western diet figure into the much higher rate
of CVD; thus how does a diet high in
sugar, refined carbs, and trans and polyunsaturated
fats cause CVD? Part of the answer is found in fatty liver
and insulin resistance and their consequences among which is an increase in ED of
the artery walls. ECs
are the gateway to atheroma (plaque) formation.[2]
Endothelial dysfunction,
a causal factor for CVD: The ECs that line the inner walls of
arteries are the gatekeepers for what enters the
underlying tissues in the arteries. Thus
damage to these cells promotes atherogenesis (development of atherosclerosis). Endothelial
dysfunction has 5 major causes,
of which 3 are associated with the Western diet.[3] 1) diet and lifestyle that causes high level
of blood sugar, especially the 7 times more reactive fructose (compared to
glucose), through the process of glycation[4] damages
the ECs. 2) Fructose is
converted to fat in the liver. The level
of glucose which controls insulin affects the rate of conversion of fructose to
fat and its storage. Thus the
combination of a diet high in sugar and refined carbs (high insulin) when
consumed long-term results in a fatty liver.[5] A fatty liver mucks up the metabolic
regulatory system to cause insulin resistance, which slows the clearance of sugars from
the blood. These causes increase the
rate of glycation which damages ECs.
3) A diet high in trans-fats and polyunsaturated fats (polyunsaturated
fats are subject to a process of rancidification in the body, in deep fryers,
and on the shelf). Their abnormal shapes
adversely affect the cell walls of the ECs (and all other cells) and thus their
function as gatekeeper to the underlying tissue. The compromised cell walls
of ECs permit bacterial
and viruses to pass through and enter the underlying tissue of the
arteries. Pathogens in the artery
wall
cause the development of AS and
their associated pathologies. The
abnormal shaped fats affect every cell in the body since they accumulate in
cells because they can’t be metabolized. They adversely affecting cellular
functions;
for a review of the evidence click on link. 4)
Carbon monoxide (mostly from tobacco) and
other reactive chemical in the blood bond to the ECs (similar to glycation).
Thus significant exposure to high levels of
blood borne reactive chemicals promotes atherosclerosis. 5) Infectious agents
through their toxins
circulating in the blood damage the ECs
(certain chronic infections are associated with CVD). In summation: these causes of damage to ECs which compromise their function as
the gatekeeper that selectively permits chemicals and cells to enter the
underlying layers of the artery; thus so damaged the ECs permit the penetration
of pathogens into the tissue within the
arteries. Infectious agents in the
artery walls have been convincingly shown to be the major cause of plaque formation
through an immune response to
their presence.[6] In conclusion, the five processes which
damage the ECs are atherogenic. 6)
Elevated homocysteine is causally associated with ED through reactive chemicals
(the details of this mechanism are
sketchy at best) and also by causing LDL aggregation (clumping) following LDL’s
reaction with pathogens or their toxins. Such
clumps it is theorized hinder the flow
of oxygen from the vasa vasorum (Uffe Ravnskov How
the Cholesterol Myths are
Kept Alive, 210). 7) The damaged ECs
are more likely to leak the underlying young plaque and thereby cause an
ischemic event that could result in myocardial
fraction,
stroke, or kidney damage-- depending on location of leak.
The Western diet with
its fructose, refined carbs, and unnatural fats has caused the CVD, T2D, and obesity pandemics.
These conditions along with strokes, heart attacks, arthritis, macular
degeneration, osteoporosis, and dementia are collectively called “the diseases
of Western society/civilization”. Tragically the food manufacturers
have successfully
exported this diet to Asia and the underdeveloped world—watch Globesity. These
manufacturers have
followed the same path as the tobacco industry has done to increase their
bottom line. This is compounded through
the active support of the pharmaceutical industry which profits from the illnesses
associated with the Western diet.
Trans & rancid fats
The cause of CVD from a 2006 review article on trans-fats: “In addition incorporation of trans-isomers
into membrane phospholipids may influence the physical properties of the
membrane as well as the activities of the membrane-associated enzymes. Several
studies suggest that trans-fats cause
ECs affects wall of arteries and other tissues]… soluble vascular-cell adhesion
factor…reflected by ruction in
brachial artery flow-mediated vasodilation by 29 percent [raises blood
pressure], as compared with intake of saturated-fats.” The 1986 ADA review
article states the
same. Both list the effects of rancid
polyunsaturated fats. Polyunsaturated fats are subjected to oxidation through
reactive products of metabolisms (ROS), and as rancid fats, like transfats the
body lacks enzymes for their metabolism.
They both accumulate in the body and muck up various systems. “Rancidification
can
produce potentially toxic compounds
associated with long-term harmful health effects concerning advanced aging,
neurological disorders, heart disease, and cancer. A combination of
water-soluble and fat-soluble antioxidants is ideal” Wiki. “Under
such conditions [of commercial frying]
both thermal and oxidative decomposition of the oil may take place. Such unavoidable
chemical reactions cause
formation of both volatile and nonvolatile decomposition products…. Various
symptoms of toxicity, including irritation of the digestive tract, organ
enlargement, growth depression, and even death have been observed when highly
abused (oxidized and heated) fats were fed to laboratory animals”… and
the article goes on “Lipid
peroxidation refers to the oxidative degradation of lipids. It is the process
in which free radicals "steal" electrons from the lipids in cell membranes, resulting in cell damage. It most often affects polyunsaturated fatty acids, because they contain multiple double bonds in between which lie methylene bridges (-CH2-) that possess especially
reactive hydrogens. If not terminated fast
enough, there will be damage to the cell membrane…” for
more on rancid fats.
[1] I must caution the reader that
Wikipedia articles on issues affecting pharma are written by pharma’s KOLs and
those accepting their tobacco science. A
case in point is the definition of endothelia
dysfunction: In vascular diseases, EC is a systemic pathological
state of the endothelium (the inner lining of blood vessels) …. Normal functions of EC
include mediation of coagulation, platelet adhesion, immune function and control of volume and electrolyte content of the intravascular and extravascular
spaces. ” The EC act as a gatekeeper as
to what can penetrate the tissue that make up the arteries, which includes both
pathogens, white blood cells, LDL, and nutrients necessary for the health of
the tissue that makes up the arteries.
See bottom of page for a discussion of what is wrong with pharma’s
description of endothelial dysfunction, including what I edited out.
[2] A second entrance to the tissue is the
vasa
vasorum a network of small blood vessels in the arteries that supply oxygen and
nutrients. The research on their role in
CVD is thin. They too are lined
with endothelial
cells. They are involved in atherogenesis,
though probably that which causes EC is also operative in the vasa
vasorum. Given both the lack of
consensus and that a discussion of this system adds little to the topic of
atherogenesis, for the sake of simplicity, I am forgoing further discussion of
the vasa vasorum’s role. Though not
mentioned, 1-5 above applies also to the vasa vasorum.
[3]
There is very strong epidemiological evidence, for example, Orientals on
traditional diets have a much lower incident of metabolic syndrome (MeS) consisting
of obesity, CVD, T2D, and IR.
Once on a Western diet, they and others populations who once were on a
traditional diet, they now all manifest all the chronic conditions associated
with Western civilization. The common
factor is the combination of fructose and refined carbohydrates. The traditional
oriental diet is high in
refined carbs, but only 14 grams of fructose.
Traditional diets are also very low in the unhealthful trans-and-polyunsaturated
fats.
[4] Glycation is the non-enzymatic bonding
(random bonding) of sugars to lipids and proteins. This bonding is damaging
to the EC that line
the arteries—glycation is more damaging to them than the short-lived red and
white blood cells. Thus part of the reason
why diabetes rate has over doubled the risk for MI lies with the higher serum
glucose level. “Some AGEs are
benign, but others are more reactive than the sugars they are derived from, and
are implicated in many age-related chronic diseases such as cardiovascular
diseases (the endothelium, fibrinogen,
and collagen are damaged)” Wiki.
[5]
Other factors contribute or reduce risk; most important are the rate of
metabolism, lifestyle, fasting, and genetics.
[6]
Pharma with their tobacco science claims that atherosclerosis is caused by an
immune response to oxidized LDL which results in plaque consisting of
cholesterol, macrophages, and LDL. These
are far-fetched (see Ravnskov supra) or click on link, and are found in
plaque. Numerous journal articles make both points;
click on this link and for a few of the published
journal articles. Thus we have 2
distortions, that concerning pathogens and that on the function of LDL.” The same finding with much greater detail is in the 1984 thorough review by the Department of Agriculture.
Why
in primitive societies are obesity virtually unknown and the diseases of
Western societies much lower?
Even among those primitive
societies that consume a significant amount of fruit and carbs there are
several differences all of which work towards remaining slim and not developing
atherosclerosis: 1) lack of steady food
supply. Fruits are seasonal, and during
dry season the diet is much different than during the rainy seasons. And even
during times of plenty, daily foods
varied more; thus these people do not prior to farming have a steady diet high
in sugars and refined carbs. 2) Wild
varieties of fruits have only a fraction
of the sugar of domestic varieties. 3)
Grains are not processed to remove the cereal germ and the bran, and most
tubers contain a significant portion of fiber; thus they have a lower glycemic
and insulin index. 4) Periodic periods
of scarcity results in energy restricted diets.
5) Physical excursion entails a lower insulin spike following a high
carb meal. 6) The literature and old
photos confirm that obesity was virtually unknown and medical records once
contact with civilization occurred before lifestyle was changed indicate that
the diseases of civilization (heart attacks, strokes, dementia, arthritis, and
cancer) were very rare if recorded at all.
Infectious diseases and violence were their principle cause of
death. The daily high sugar (fructose)
Western diet has no equivalent among paleo societies.
Fix for ED
What
is to be done: The fix is simple to
get off the Western diet
and exercise. For detail recommendations
on supplements and on 3 diets depending on state of health
Evidence
for the fix is scattered throughout the above
material. In short to avoid the Western
diet with its unhealthy combination of sugar (fructose) and refined carbs and
the trans-and-polyunsaturated fats.
Given
the wide variation in the readers’ health, I have an
article, Concise Diet, that
covers all situations, at In addition that are some worthy supplements
(from bottom of Concise Diet): “Besides
the healthful diet describe above and exercise, several supplements have
significant health benefits. Best are aspirin
325 mg, CoQ10,
vitamin C,
& omega-3 fatty acids fish oil—in that
order. All 4 reduce very significantly
the risk for CVD & other chronic
conditions. In sufficient dose
Natural
hormone replacement therapy
(NHRT) estradiol for women and for
elderly men testosterone;
they slow down the aging process and reduce
the risk of chronic conditions. These
hormones ALSO promote weight control and the motivation to exercise. For more
info on statins, cholesterol myth,
CVD,
carbs,
fats,
and a video
library
click on
links. The video page
has documentaries and books that confirm my
claims. Click on Junk treatments
to find out
how pharma manipulates the practice of medicine. You ought to take better
care of your body
than your car.
Bad
Pharma on Endothelia Dysfunction:
I must caution the reader that Wikipedia articles on issues affecting
pharma are written by pharma’s KOLs
and others who accept pharma’s tobacco science.
A case in point is the definition of endothelia
dysfunction: In vascular diseases, EC
is a systemic pathological state of the endothelium (the inner
lining of blood vessels) and can be broadly defined as an imbalance between vasodilating
and vasoconstricting
substances produced by (or acting on) the endothelium.[1] Normal
functions of ECs include mediation
of coagulation,
platelet adhesion, immune function and control of volume and electrolyte content of the
intravascular and extravascular spaces.”
The article Wikipedia article states:
”Endothelial dysfunction is
thought to be a key event in the development of atherosclerosis” thus implying that hypertension causes AS, rather than AS
causes hypertension. Thus the treatment
for ED so as to prevent AS is to
lower blood pressure. Pharma
makes billions treating hypertension, thus the reference to imbalance, which
they correct with drugs. Unfortunately treating symptoms is not treating the
cause and thus patients do not significantly benefit from treating hypertension
with drugs, except for the population with malignant
hypertension
(above 180 over 110). Pharma makes
billions treating those who don’t
benefit from hypertension drugs.[1] Hypertension is a sign of atherosclerosis,
like fever is of influenza, thus treating it only reduces the discomfort caused
by elevated blood pressure (if there is any), it doesn’t affect the underlying
cause atherosclerosis and the risk for ischemic events.
Given
that there is no reliable test that
measures ED. Current test measure
factors associated with AS.
This entails that pharma is creating another condition, ED, that promotes
drug sales.
[1]
Again I must caution
that the Wikipedia article is grossly distorted by leaving out the role of
atherosclerosis, hard, swollen, stiff arteries.
Most of the pathological developments associated from malignant
hypertension result from thrombolysis, the leaking of young, unstable plaque
from atherosclerotic arteries.
^^^^^^^^^^^^^
supplemental journal article
^^^^^^^^^^^^^
Except for parts in courier
new all that
is below is taken from the journal article.
http://diabesity.ejournals.ca/index.php/diabesity/article/view/19
Online First: October 15, 2015
abstract
Hyperinsulinemia: A
unifying theory of chronic disease?
Abstract:
Globally, there is an
increasing prevalence of non-communicable diseases. The morbidity and mortality
from these conditions confer a greater Economic societal burden.
Epidemiological research associates insulin resistance in the etiology of these
diseases, but there is limited evidence for the mechanism of damage. Emerging
research suggests that hyperinsulinemia, a symptom of insulin resistance, may
cause these pathological changes, and therefore be an independent contributor
to these diseases. This review shows that hyperinsulinemia, or excessive
insulin secretion, should be considered independently to insulin resistance,
defined as glucose uptake rate, even though the two conditions are intertwined
and will co-exist under normal conditions. Hyperinsulinemia directly and
indirectly contributes to a vast array of metabolic diseases including all
inflammatory conditions, all vascular diseases, gestational and type-2
diabetes, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, obesity and certain cancers and
dementias. The mechanisms include increased production of: insulin growth
factor-1; reactive oxidative species and advanced glycation end-products; and
triglyceride and fatty acids. Hyperinsulinemia also directly and indirectly
affects many other hormones and cytokine mechanisms including leptin,
adiponectin and estrogen. There is limited research standardizing the
hyperinsulinemia diagnostic process. Methodological concerns and lack of
standardized reference ranges preclude the use of fasting insulin. Most
research has also focused on insulin resistance and it is unknown whether these
methods translate to hyperinsulinemia.
Complete article sections thereof. Comments by JK are in Courier New and/or
brackets
http://docs.google.com/viewer?url=http://diabesity.ejournals.ca/index.php/diabesity/article/viewFile/19/61 Long
The mechanisms include increased production of: insulin growth factor-1;
reactive oxidative species and advanced glycation end-products; and
triglyceride and fatty acids. Hyperinsulinemia
also directly and indirectly affects many other hormones and cytokine
mechanisms including leptin, adiponectin and estrogen. There is limited
research standardizing the hyperinsulinemia diagnostic process. Methodological
concerns and lack of standardized reference ranges preclude the use of fasting
insulin. Most research has also focused on insulin resistance and it is unknown
whether these methods translate to hyperinsulinemia [p 34].
From this article Fructose: Fructose is metabolized in liver into ATP and/or triglycerides in a
process that is competitive with, and preferential to, glucose. If excessive
fructose is consumed, glucose will not be metabolized causing hyperglycemia and
subsequent hyperinsulinemia.20, 21
Excessive fructose also results in hyperuricemia which is associated
with reduced endothelial nitric oxide causing vasoconstriction, endothelial
dysfunction and insulin resistance 21 [p 35-36].
Medication-induced: There are
a number of medications known or suspected to cause hyperinsulinemia and/or
contribute to insulin resistance. Exogenous corticosteroids (prednisone) and
exogenous insulin and insulin ecretagogues (sulphonylureas) have had their
mechanisms discussed. Other medications include the antipsychotics (e.g.
clozapine), and statins.27
[Thus the use of statins has been found
to significantly increase the risk for T-2-D]. The mechanisms for these medications causing hyperinsulinemia are currently
unknown. Due to the nature of insulin
receptor regulation, it is also plausible that insulin sensitivity of the cells
can be restored. This would require the absence of both hyperinsulinemia and
hyperglycemia. Case studies indicate
that a carbohydrate restricted diet may facilitate this effect.10 Overall, it should be recognized that hyperinsulinemia
is independent to insulin resistance: Hyperinsulinemia
is excessive insulin secretion, while insulin resistance is impaired glucose
uptake, p 36.
As shown in Table 1, hyperinsulinemia can be mechanistically
and epidemiologically linked
to metabolic syndrome, gestational and type 2 diabetes and therefore,
cardiovascular and other diseases with an increased prevalence in those with
metabolic syndrome.2-4, 28 It is also an independent risk factor for
a number of other diverse conditions including diet-induced obesity,
steoarthritis, certain cancers, especially breast and colon/rectum, disease and
other dementias.5, 6, 29-32 Hyperinsulinemia
affects the body via five main
mechanisms: Increased reactive oxidative species and advanced glycation
end-products; increased insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1); hyperglycemia;
increased fatty acid/triglyceride production; and by affecting different
hormones and cytokines p 36.
On page 37-8 is a table of
conditions associated with ED and the mechanism of causation with references to
journal articles divided into mechanical (modus operandi) and epidemiological
(population studies).
|
BIOLOGICAL
SYSTEM
|
DISEASE
|
|
Cancer
|
Breast, ovarian, colon, bladder, pancreas, liver
|
|
Circulatory
|
Atherosclerosis, cardiomyopathy, endothelial dysfunction, thrombosis
|
|
Endocrine
|
Chronic inflammation, obesity
|
|
Gastrointestinal
|
Diabetes type 2 and gestational, hyper-triglyceridemia,
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
|
|
Nervous
|
Alzheimer’s and vascular dementia, peripheral neuropathy,
retinopathy
|
|
Skeletal
|
Osteoporosis (caused by collagen breakdown and menserchymal cell
compromise
|
|
Urinary
|
Nephropathy (microvascular diseases, microaneurysm formations,
etc.).
|
|
|
|
Polyunsaturated
fatty acids are considered very susceptible to reactive oxidative species
damage, triggering
lipid peroxidation,
which can affect cell membrane fluidity and integrity, potentially being the
mechanism for endothelial damage.
Amino acids such as cysteine and
methionine are very susceptible to reactive oxidative species damage.
Changes to these amino acids are implicated in the development of Alzheimer’s
disease.
Insulin, IGF-1 and other substances such as vascular endothelial growth
factor (VEGF) can stimulate the growth and division of many cells… cancer cell
proliferation and metastasis29 [p 38].
Hyperinsulinemia is also believed to elevate plasminogen activator
inhibitor type-1 (PAL-1) levels, with associated increased fibrinolysis and
increased risk of thrombosis. When combined with the increased coagulation from
hyperglycemia, this may explain why over 80% of people with type 2 diabetes have
a thrombotic death [p 39].
|